Are you looking for a complete, ultimate SEO checklist to kick off your digital marketing? You’ve come to the right place.
If you'd prefer to read this guide as a PDF eBook click here.
SEO is the best (and cheapest) marketing you will ever do and it can bring a whole load of prospects to your website month after month.
Here’s a snapshot of how HubSpot have grown their blog traffic over the past 2 years!
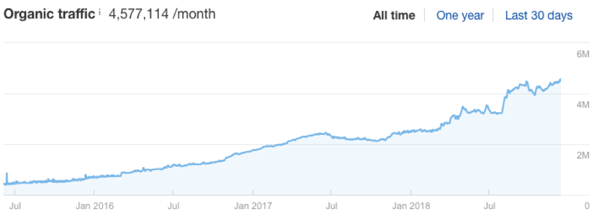
We’ve hand-picked the top 33 tips that will get you well on your way to organic search success.
You can think of these tips like fundamental principles that are applicable to any website in any niche or industry. In other words, you can trust them because they work and always will. No need to worry about black hat or grey hat methods here. This is all 100% white hat!
Feeling a little overwhelmed? Don’t. Most of these tips are super easy and remember that some are definitely more important than others.
Let’s get into it step by step.
SEO basics
These SEO basics should be done before anything else. They won’t necessarily get you onto page 1 of Google but they’re still really important for SEO.
1. Setup Google Search Console
Step 1 is to setup Google Search Console so that you can monitor crawl errors, performance and insights like which search queries your customers are using in Google. What’s awesome is that it’s totally free! Thanks Google 😉
To set up Google Search Console, first you need to log into your Google account and then you have to verify ownership of your website. The easiest way to do this, is to add a supplied <meta> tag to the <head> section of each page of your site. If you’re using WordPress, this is really easy to do using the Insert Headers and Footers plugin.
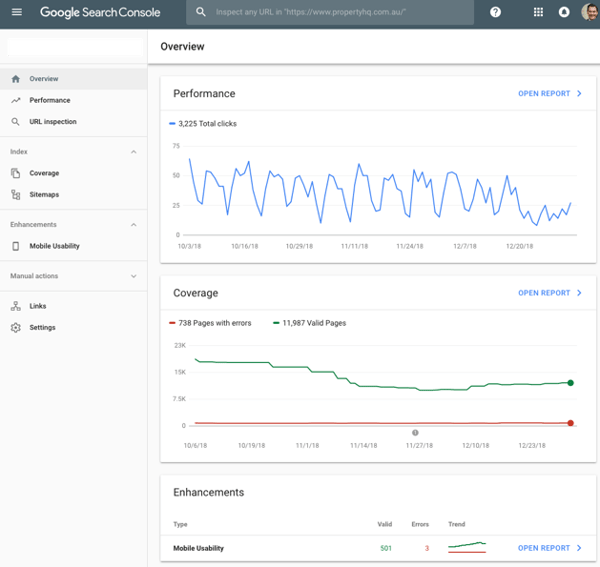
Google Search Console helps you to measure your website’s search traffic, track performance, fix issues, submit a sitemap and even see the exact “queries” that your customers are typing into Google. You can also check how mobile-friendly your website is. This is super important as it’s a Google ranking factor!
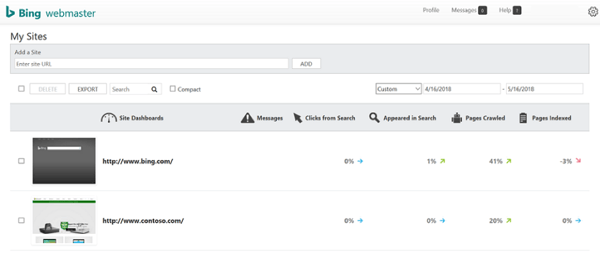
2. Setup Bing Webmaster Tools
Next, it’s important to also setup Bing Webmaster Tools. Not quite as popular as Google but it’s still worth the effort as it gets 30% of all search traffic.
Like Google, you’ll need to login using your Microsoft, Google or Facebook account and then verify site ownership in a similar way. Upload that <meta> tag and you’ll be on your way!
3. Setup Google Analytics
Another free tool provided by Google is Google Analytics. A REALLY powerful tool that provides a deep understanding of your website visitors. With almost endless data and reports, Google Analytics will bring out the data nerd in everyone!
It provides a bunch of great data, like how much website traffic you’re getting from Google, which pages are bringing in the most traffic, which sources are generating the most traffic (e.g. organic search, paid search, direct), what your website engagement is like (e.g. bounce rate, time on site), conversions and loads more.
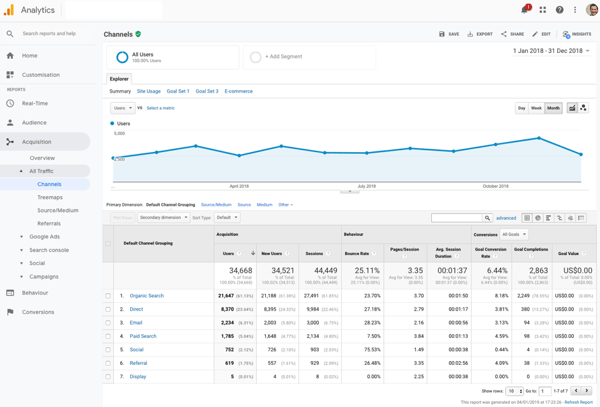
When you link it to your Google Search Console and Google Ads accounts, you’ll be able to see even more insights that can help drive business goals. Like Search Console, you’ll need to install a tracking code on your website to capture information in Analytics.
Here’s a great video that takes you through each step.
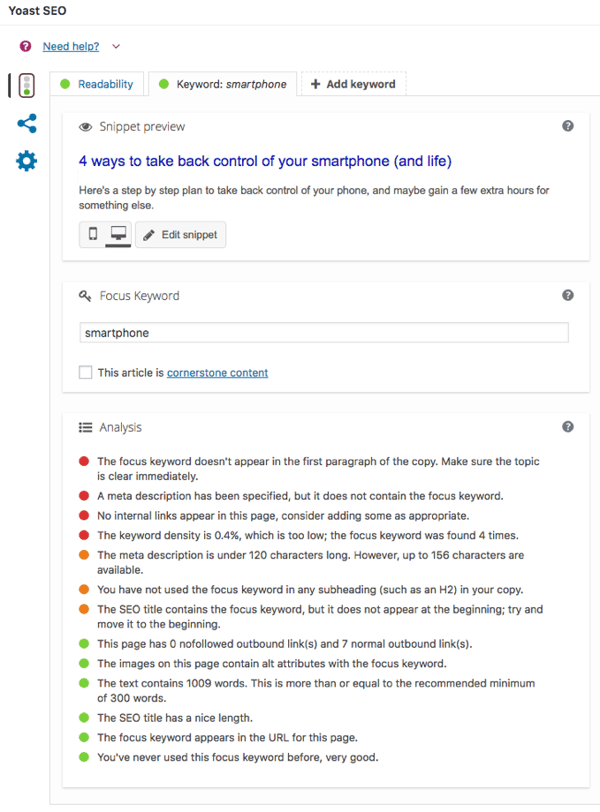
4. Install Yoast SEO
Yoast is an awesome plugin for WordPress (and a few other CMS’) which makes SEO a LOT easier to manage. Yoast makes it super easy to do on-page optimisation across your website, submit sitemaps, check readability, monitor internal links and keyword density and a lot more.
5. Create a sitemap
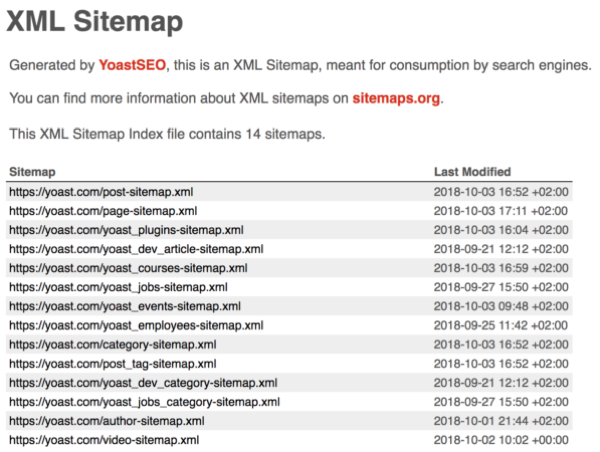
Sitemaps help Google and other search engines to crawl and index pages on your site. You can see your sitemap (if you have one) by searching yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml.
Plugins like Yoast make it really easy to set these up! There’s a bunch of other sitemap generators out there also.
6. Create and add a robots.txt file to your site
A robots.txt file tells Google and other search engines which pages they can index and which pages they can’t. In fact, the robots.txt file will include a link to your sitemap
It will typically look like this.

The above robots.txt example would allow all search engines to crawl your entire site.
Check to see if you already have a robots.txt file on your site by navigating to yourdomain.com/robots.txt.
Yoast has an in-built robots.txt file. If you don't have Yoast, here's an excellent robots.txt generator that's easy to use.
If you’d like to learn a little more about robots.txt, Yoast has a great guide about all things robots.txt.
Keyword research
Keyword research is the foundation of SEO. If you don’t know what people are searching for, how will you know what to write and optimise? Here’s some tips to get you started.
1. Focus on topics not keywords
Because of the increase in mobile and voice search, Google has evolved to better understand what people are searching for. Google’s Hummingbird algorithm update in 2013 really brought this home by focusing on phrases instead of fragmented keywords. This marked a major change from keyword to topic-focused SEO.
Think about your business and list 5-10 topics that you think are important. For a digital marketing agency like us, topics could include “email marketing,” “seo,” “social media” and so on. These topic buckets will help you in the next step.
2. Add keywords to your topics
Now that you have some topics, it’s time to find keywords that fall into each of these buckets. A great way to provide some inspiration here is using Google’s “Searches related to [topic]” at the bottom of the search results. For example, if you do a search for “seo” which is a topic, Google will provide the following related searches.
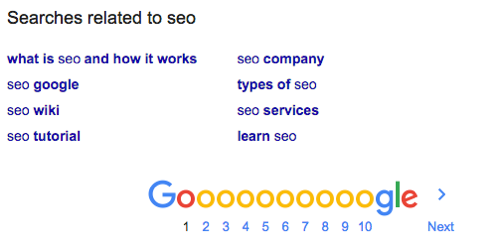
You can do this step for each topic bucket to get a bunch of great keyword ideas. You can take this even further by typing in these related searches and looking at their related search terms!
3. Include a mix of head, body and long-tail keywords
If you don't know the difference between head, body and long-tail keywords, let me explain.
Head terms are usually single-word keywords phrases with huge amounts of search volume and competition — think “insurance.” Because head terms are so broad, they’re more “top-of-the-funnel” and they don’t convert as well.
Body keywords are 2-3 word phrases that get decent search volume, but are more specific than head keywords. Keywords like “conference venues sydney” are examples of body keywords. These almost always have lower competition than head keywords but can still be very competitive.
Long-tail keywords, on the other hand, are longer keyword phrases usually containing four or more keywords that are super specific. Even though they get less search volume individually than head or body keywords, when added together, they make up the majority of searches online. They’re also further down the funnel and great for conversions.
It's a good idea to have a mix of head, body and long-tail keywords, because it'll give you a keyword strategy that's well balanced with long-term goals and short-term wins.
4. See what keywords you’re already ranking for
If you’ve had your website for a while, you should already be ranking for a few hundred keywords.
A great way to check this is to use Google Search Console which tells you exactly what “Queries” or keywords, people are typing into Google. Google Search Console shows your average position for each of the keywords you rank for and how many impressions and clicks this brings you.
If you’d like to dig a little deeper, Ahrefs has an awesome tool that allows you to see what keywords you’re currently ranking for. You can sort by location, search volume and ranking.
5. See what keywords your competitors are ranking for
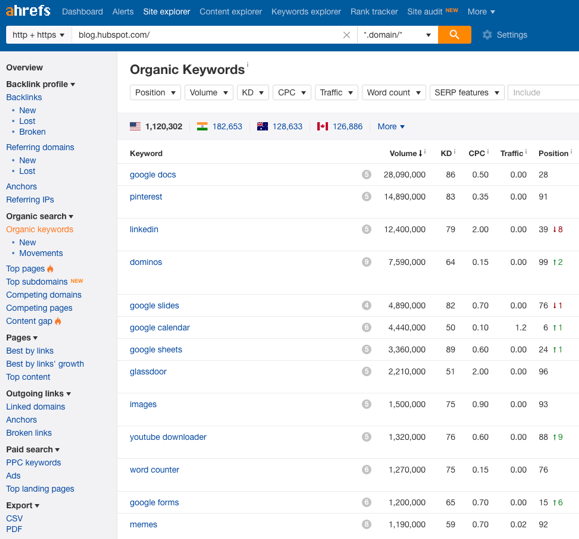
Chances are, your competitors have already performed a lot of time consuming keyword research work for you. So why not research which keywords they’re ranking for and pick the best ones! If you don’t know who your competitors are, just put your keywords into Google and see who ranks on the front page.
You can use a tool like Ahrefs that allows you to see what keywords pretty much any website is ranking for. You can sort by location, search volume and ranking. List out the top keywords for each competitor that you’d also like to rank for and you’re on your way!
6. Use keyword research tools and shortlist
Your spreadsheet is probably already full of a bunch of topics and keywords from the above steps. If you need some more keyword ideas, there’s a few great tools that can help:
Google Trends visualises how search trends change over time. Enter a keyword, and you will see the relative popularity of that search query over the past 12 months.
But Google Trends has another cool trick up — related queries. Drop down to the bottom of the page and you’ll see a “Related queries” box.
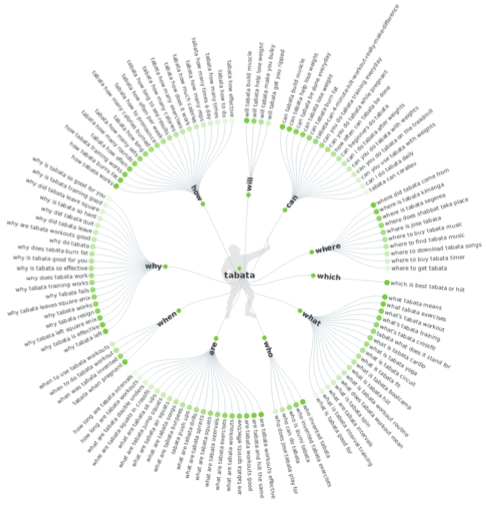
Answer the Public finds questions, prepositions, comparisons, alphabeticals, and related searches.
Here’s an example using the seed keyword “tabata” — as in the cardio workout 😀 As you will see, quite a few keyword ideas there!
In SEO circles, Google’s Keyword Planner gets a bad rap because they removed exact monthly search volumes and replaced it with a vague range. Having said that, it comes from Google, so it’s still super useful and accurate.
See an example below for “best 4k tv”.

Personally, I use all of these, along with Ahrefs Keyword Explorer which is amazing. I’ve also used Moz’s Keyword Explorer. Both are great and provide a tonne of keyword ideas to get you started.
Technical SEO
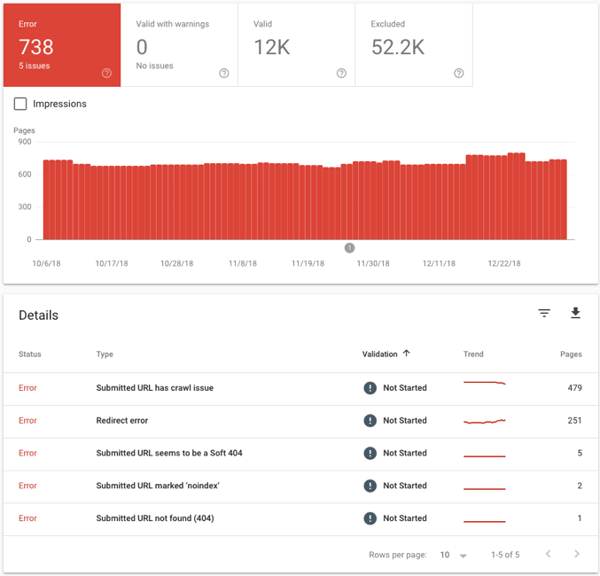
1. Identify crawl errors
A crawl error means that Google is having trouble viewing and therefore indexing a page on your site. Not good. If Google can’t see it and index it, you’re not going to rank for it.
Google Search Console helps out here by providing a list of pages that have various crawl errors, whether that’s a 404 error, redirect error or something else. It’s good practice to keep a close watch and fix any crawl errors regularly.
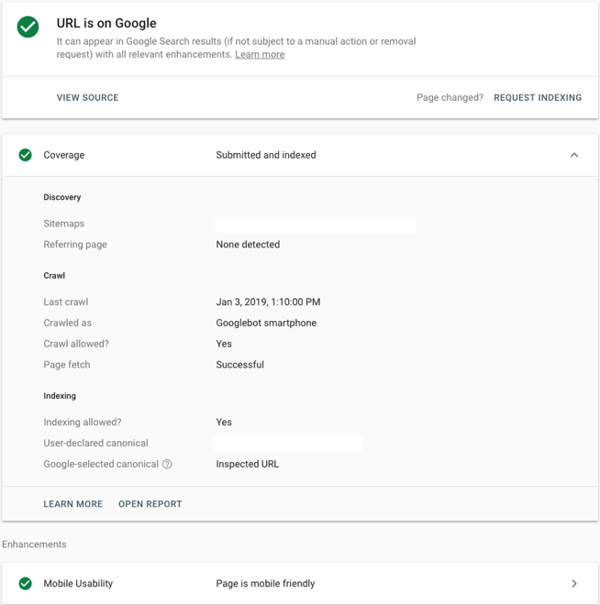
2. URL inspection (Fetch as Google)
For the same reasons as crawl errors, if Google can’t see everything on your page, it won’t rank it. Again, Google’s Search Console comes to the rescue here. It has a feature called “URL inspection” (formerly Fetch as Google) which provides information about the last time it was crawled, if Google could render the page correctly, whether the page has been indexed and more.
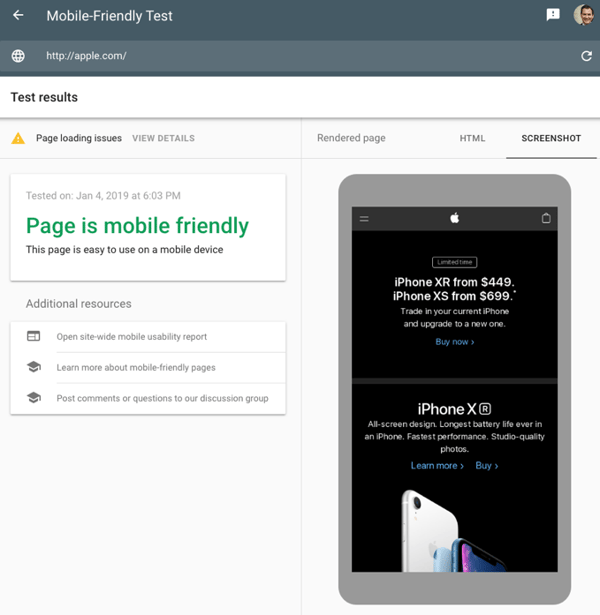
3. Make it mobile-friendly
Google announced in early 2018 that they had rolled out mobile-first indexing. In a nutshell this means that if your website is not optimised for mobile, it won’t rank.
Google have provided a free tool that tests whether your website is mobile-friendly from Google’s point of view. Google’s Search Console also provides some insights here, in its “Mobile Usability” feature — specifically what is detracting from your site’s mobile usability. Google even provides tips on how to fix it.
4. Use HTTPS
Another Google ranking signal is HTTPS, which was announced back in 2014. HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is an internet communication protocol that protects the integrity and confidentiality of data between the user's computer and your site. It uses Transport Layer Security protocol (TLS), which provides encryption, data integrity and authentication.
Here’s a great list of reasons to switch to HTTPS for any sceptics out there! For sites that don’t have HTTPS, you’ll notice a big, fat “Not secure” page courtesy of Google Chrome and Firefox which kicked in from mid-2018.
Thanks to the folks at Let’s Encrypt an HTTPS is even free! The good news is that HTTP is really easy to set up. Just get a certificate, activate it, install it and you’re done.
Below is an example of a website — one of the most visited sites in Australia — that should really have a HTTPS.

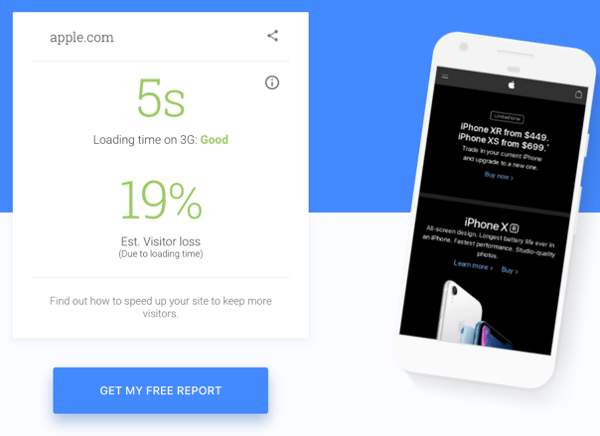
5. Make sure your site is lightning-fast
Another thing that Google loves is a fast site. Although page speed has been a ranking factor for a while, it was previously focused on desktop searches. Since July 2018, page speed is also now a ranking factor for mobile searches.
Again our friends at Google are providing a helping hand here, through their recently updated PageSpeed Insights tool (which has now been integrated in Google Search Console). The tools provides some great data around page speed and some opportunities to further improve page speed.
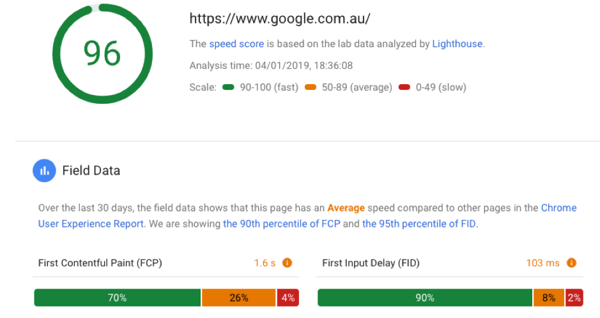
Google’s think with Google tool also provides some mobile page speed insights, industry comparison and some recommendations.
6. Fix any duplicate content issues
Duplicate content occurs when you have two or more similar or identical pages on your website. This can cause problems because Google does not know which page it should rank.
Whenever content on a site can be found at multiple URLs, it should be canonicalised for search engines. The easiest way to do this is to set up a 301 redirect from the "duplicate" page to the original content page.
7. Fix broken links
Broken links are bad for user experience. And user experience is something that Google cares deeply about—in fact, they recently announced that RankBrain is their third most important ranking signal. Kind of a big deal.
RankBrain pays very close attention to how you interact with the search results. Specifically, it’s looking at click-through-rate, time on site, bounce rate and other user experience signals (UX signals).
Broken internal links also waste “link juice,” which can have a direct adverse effect on your rankings.
A simple Chrome extension like Check My Links can quickly identify any broken links on your page. You can also use Google Search Console’s “Coverage” report which lists out any URLs that have errors.
On-page optimisation
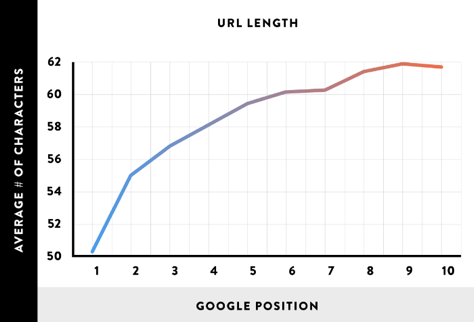
1. Descriptive and short URLs
Your URL helps Google to know what your page is about, so make sure you include your targeted keyword in your URL. Your URLs should also be descriptive and they should provide some insight into what people should expect when they click through to your page.
But be sure to keep your URLs as short as possible. Why do I say that? A recent analysis of 1 million Google search results found that short URLs rank best in Google.
2. Compelling title tag and meta descriptions
Once you’ve optimised your URL, the next step is to write your title tag and meta description.
When it comes to title tags, it’s best practice to “front-load” your title tag with your targeted keyword.
You also need to remember that your title tags and meta descriptions are like advertising — so make them work for you! Crafting compelling titles and descriptions will increase your click-through-rate (CTR) and bring more traffic to your site. This in turn will send some great user experience (UX) signals to Google which will help you rank.
If you’re using Yoast, you can do this really easily using their plugin.
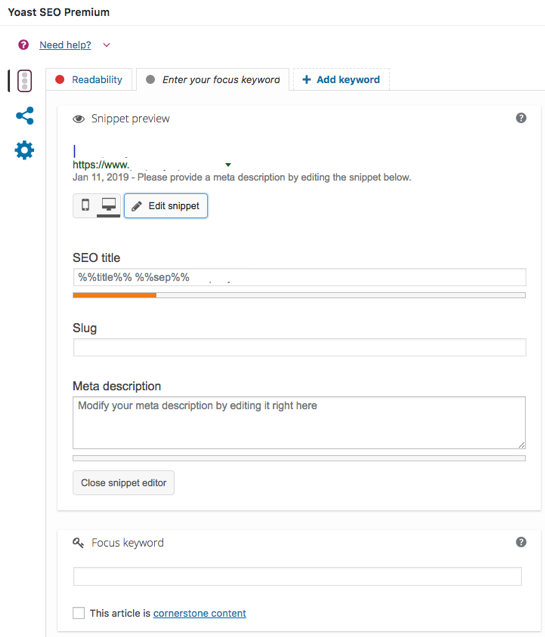
3. Optimise your H1, H2 and H3 tags
It’s also best practice to optimise your H1, H2 or H3 tags for your targeted keyword. This reinforces to Google what your page is all about and it helps people to quickly understand that they’re in the right place.
Having said that, according to a 2016 study of 2M keywords by Ahrefs, ~85% of top‐ranking pages don’t have their keyword in the H1 tag.
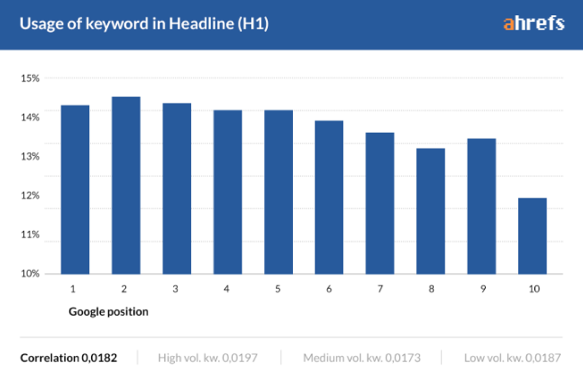
So this tip may not move the needle as much as other ranking factors, but it all helps!
4. Descriptive “alt” tags for your images
The purpose of alt tags is to offer some context to the reader, should the image fail to load (or if the visitor is using a screen reader). That’s why you should make your alt tags descriptive — which often means including your targeted keywords also.
Alt text is also really important for Google Images which can bring a lot of traffic your way. Below is an example from Google Search Console.
5. Don’t forget internal and external links
Research shows that linking to trusted, relevant and authoritative websites like Wikipedia and others can also help your rankings. This tells Google that your content similarly well-referenced and credible.
What about linking to other pages on your own website? This is a really easy way to share some “link juice” from your page with other pages and help your website rank better overall. Aim to link to at least 2-3 other pages as a minimum. Wikipedia are really good at this!
6. Use your targeted keyword in first 100 words
To make Google’s job even easier, use your targeted keyword in the first 100 words of your page. Along with all of your other on-page optimisation, this reinforces to Google what your page is about and helps your ranking chances.
7. Use synonyms and LSI keywords
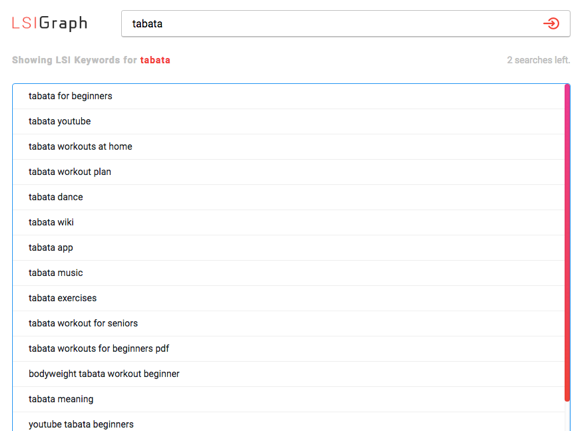
Using synonyms and LSI keywords that are related to your targeted keyword, your page will read less spammy, it will sound more natural and Google will love it. Why? Because Google use LSI keywords to determine a page’s relevancy.
A great tool to use is LSI Graph which helps you to find stacks of related keywords that you can use in your content. Here’s some ideas using the seed keyword “tabata.”
8. Add schema markup
Schema markup helps search engines to better understand your content. It also increases click-through-rates and it can make a big difference how your page is displayed in the SERPs.
According to John Mueller of Google, "there's no generic ranking boost for SD [structured data] usage." "However, structured data can make it easier to understand what the page is about, which can make it easier to show where it's relevant (improves targeting, maybe ranking for the right terms)."
Here’s a page with schema markup that currently ranks for “removalist melbourne.”
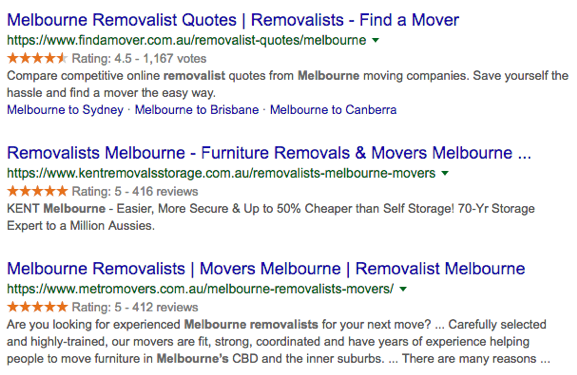
It can be a little tricky to set up, but Google’s Google’s Structured Data Testing tool can really help.
Content
If your content is average, all of the above work choosing the right keyword, getting your technical SEO right and nailing your on-page SEO, isn’t really going to move the needle for you. Great content is a key part of any SEO strategy.
Here’s a few tips that can definitely point you in the right direction.
1. Write a compelling intro
If your content isn’t up to scratch, you’ll find that within a few seconds, people will hit the back button and continue searching in the SERPs. It’s known as “pogo-sticking” and it’s not good.
So how can you avoid it? By writing a compelling introduction that captures attention, builds trust and offers a solution to the person’s problem.
Just like your headline will make or break your content, your introduction will make a big impact on the engagement of your reader. This impacts time on site and other user engagement metrics, which form part of Google’s algorithm.
2. Keep it simple and readable
Unless you’ve gone back to the 1990s, no one likes giant blocks of text.
So keep your content bite sized and break it up with subheadings, images, quotes, video — anything that will keep your readers engaged.
Here’s an example of just that from the Backlinko blog.
Unless you want to alienate half of your readers, you also need to write in a way that is understandable. This means avoiding jargon, using simple language and avoiding unnecessary adjectives and adverbs.
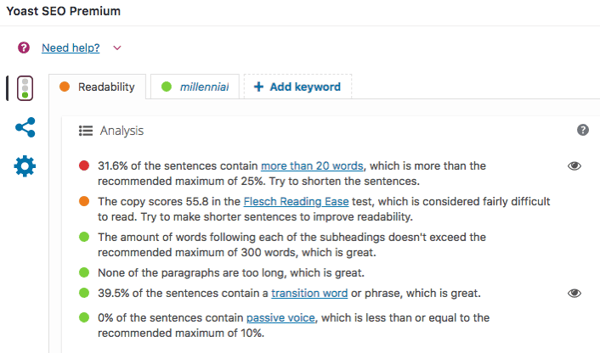
Flesch Reading Ease was created in 1948 as a readability test. The score on the test will tell you roughly what level of education someone will need to be able to easily read a piece of text.
Text with a very high Flesch reading ease score (about 100) is straightforward and easy to read, with short sentences and no words of more than two syllables. Usually, a reading ease score of 60-70 is considered acceptable/normal for website content.
If you’re using the Yoast plugin, the good news is that they have an in-built “Readability” score using the Flesch Reading Ease method which makes it really easy to check (and improve) your readability as you’re going.
3. Make your content 10x better
With millions of web pages out there, if your content isn’t better than everything else out there, it’ll struggle to rank.
This was confirmed by some research undertaken by Backlinko, which confirmed that the content that ranks the best in Google, tends to cover an entire topic in-depth.
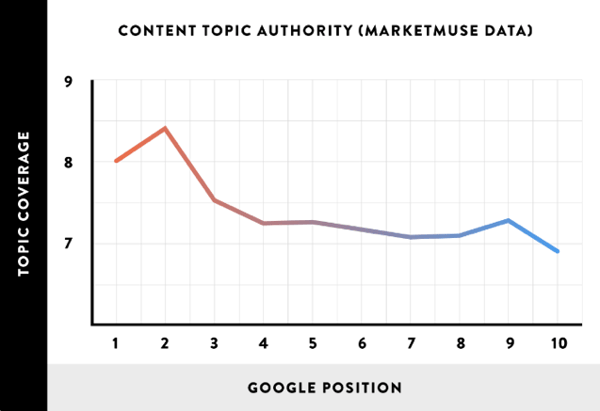
So focus on 10x content that answers everything about a particular topic. This content becomes your “pillar” or “power” page that is key to getting traction with your content marketing efforts.
Link building
Link building is definitely one of the most difficult parts of SEO. It’s often very time consuming and much of it is out of your control. But SEO without link building is really a waste of time. Why do I say that? Because backlinks are one of the top 3 ranking factors for Google. Without backlinks, your content (no matter how awesome it is) will struggle to rank.
Here are some quick wins that can help you to get some links quickly.
1. Replicate your competitor’s links
Your competitors likely have at least some backlinks. Maybe they’re from their clients, business directories or somewhere else.
Why is this a good place to start? Because if someone is linking to your competitor, it might make sense for them to link to you too.
Using tools like Ahrefs, you can easily see who’s linking to your competitors but not to you (yet).
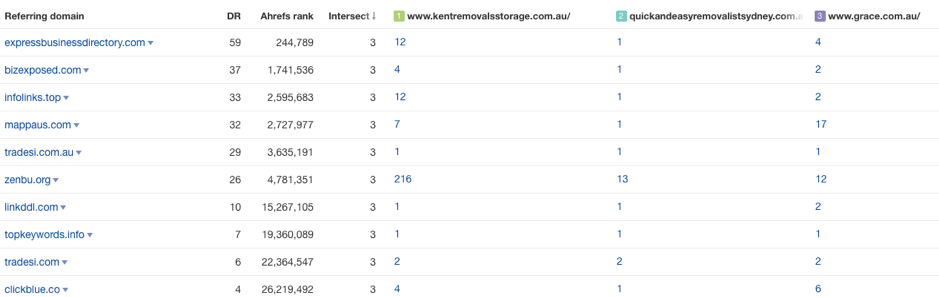
You won’t be able replicate all of their links, so look for the low-hanging-fruit — links that will be easier to obtain. These might include those from guest posts, link roundups, forums, directories and so forth.
2. Follow up unlinked brand mentions
This tip is one of the easiest ways to get some backlink runs on the board fast. Depending on your business and brand awareness, from time to time, you might be mentioned online. Often these “mentions” don’t include a link back to your site.
There’s a bunch of tools that can help you to monitor these mentions, along with good old Google Alerts which is free.
Once you’ve discovered some unlinked mentions, reach out to the authors and request that they “make your business name clickable.” Because they’re already familiar with your brand, there’s a high chance that they’ll happily make that change for you.
3. Link outreach
If you have great content to share, you can’t simply adopt a “publish and pray” approach. In other words, you can’t just write some content and hope that you’ll miraculously attract some backlinks with zero effort — wouldn’t that be nice though?
Email outreach is one of the main ways to build quality links and to do it, you need to know how to reach out to. They’re often nicknamed “linkreators” or “linkerati.” These guys are super important because they are likely to be interested in your content AND they have the ability to link to you.
It can be time consuming and complicated but if you can master it, you’ll almost have backlinks on tap! Here’s an awesome post from Ahrefs about it.
Conclusion
This checklist is 4,000+ words, but it honestly could’ve been double or triple the size. There’s heaps of actionable tips in here, but if you’re feeling a bit overwhelmed, just tackle one point at a time.
It’s true that SEO is ever-changing, but by applying this 33-point checklist, you can be confident that you’re ticking all of Google’s ranking factor boxes and you’re well on your way to SEO success!
Nathan Reiche
Nathan is the CEO and Founder of Content Chemistry, a digital marketing agency and a HubSpot Platinum Solutions Partner. He has over 15 years' marketing experience in Australia and Europe, working both on the client-side and as an agency. He's passionate about content/inbound marketing, SEO and sales funnels. And yes he's been told that he looks like Roger Federer.
